The outbreak of COVID-19 forced medical institutions to embrace Telemedicine App Development as an alternative way of providing healthcare services to limit coronavirus exposure. Telemedicine Apps with doctor-on-demand features have found great use among hospitals, physicians, patients, and the medical community.
Custom telemedicine apps have already become a must-have for medical organizations not only due to the pandemic crisis but also their useful doctor-on-demand functionalities that significantly increase access to healthcare services in areas with medical care shortages and enable clinicians to better and easier manage patients.
COVID-19 has caused a massive acceleration in the use of telehealth. Consumer adoption has skyrocketed, from 11 percent of US consumers using telehealth in 2019 to 46 percent of consumers using telehealth in 2021. The number of people who agree to consult a doctor online is still growing.
McKinsey
Telemedicine app development is demonstrating an impressive rise. Statista’s report shows that, in six years, the global telemedicine market will grow almost four times. That means that entrepreneurs have recognized the advantages of doctor-on-demand apps for both doctors and patients and started to embrace telemedicine solutions massively.
Doctors on Demand: Telehealth and Telemedicine Apps
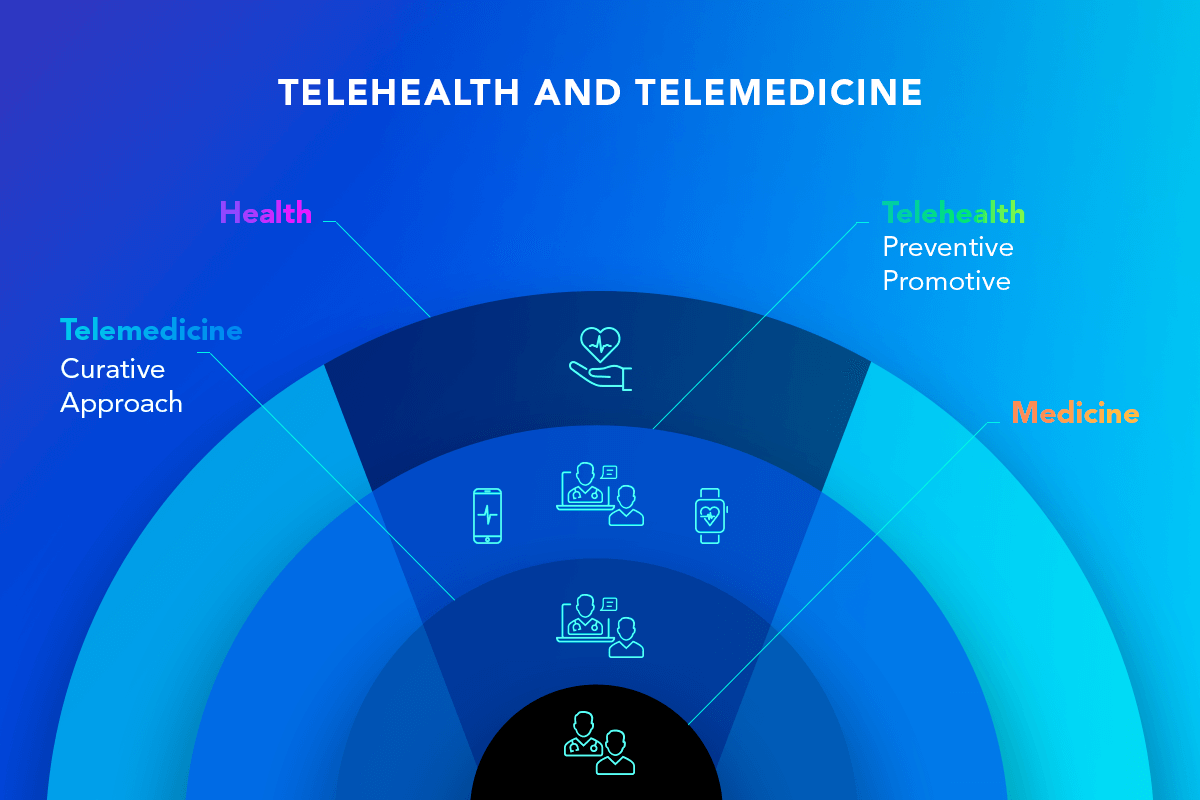
Although “telehealth” and “telemedicine” are often used interchangeably, they are not absolute synonyms. Telehealth refers to a broad field of medical solutions based on telecommunication technologies. In contrast, telemedicine apps embrace only clinical services employing electronic communications and software to provide clinical services to patients without an in-person visit.
Examples of telehealth apps:
- Personal health apps for self-management
- Personal health records apps
- Public health apps
- Video-conferencing platforms for medical education
Examples of telemedicine apps
- Remote monitoring apps
- Doctor-patient collaboration apps
Types of Telemedicine Apps
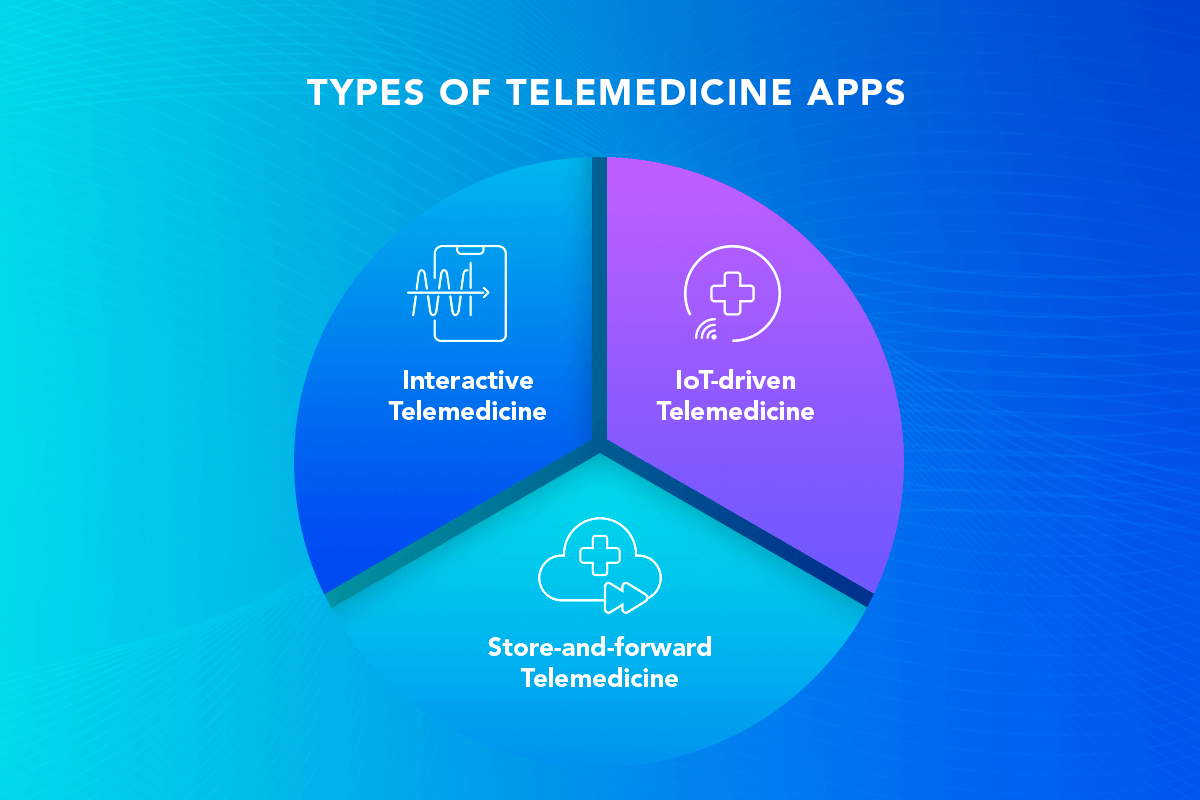
Interactive Telemedicine
Interactive telemedicine app development refers to a collaboration app that uses audio and video signals in order to connect users for a consultation. Such telemedicine apps provide follow-ups after a patient is discharged from a hospital, pharmaceutical consultations, virtual doctor visits, and monitoring of rehabilitation processes.
Interactive telemedicine covers such medical fields as Teleradiology, Telepsychiatry, Teledermatology, Teleophthalmology, Telenephrology, Teleobstetics, Teleoncology, Telepathology, and Telerehabilitation.
IoT-Based Telemedicine
Abbreviated as IoT, the Internet of Things is a network of interrelated objects, devices, and sensors that can interact and exchange huge data sets over the Internet. As IoT devices have become widespread, advanced IoT solutions have found their use in the entertainment segment and the medical context.
According to Accenture, the use of wearable devices shifts from fitness trackers towards health management, with telemedicine gaining a new level in remote health monitoring.
IoT-powered devices can be applied to measure the following:
- Blood pressure;
- Levels of sugar;
- Heart rate;
- Falls from a chair or a sofa;
- Other health conditions.
The obtained data automatically synced with an app or manually added to the existing medical records by the patient are made available for doctors.
Read more about IoT solutions in the time of COVID-19.
Store-and-Forward Telemedicine
Store-and-forward telemedicine apps refer to a secured platform that allows patients and doctors or medical providers located afield to forward and share medical data, such as lab results or medical records. Store-and-forward telemedicine is asynchronous. It is aimed at collecting clinical information, including records about blood pressure, levels of sugar, heart rate, etc., for a subsequent electronic transfer for evaluation. In addition, patients’ audio, video, and image content can be stored and then sent to their physicians for further analysis.
Telemedicine App Development: Features and Functionalities
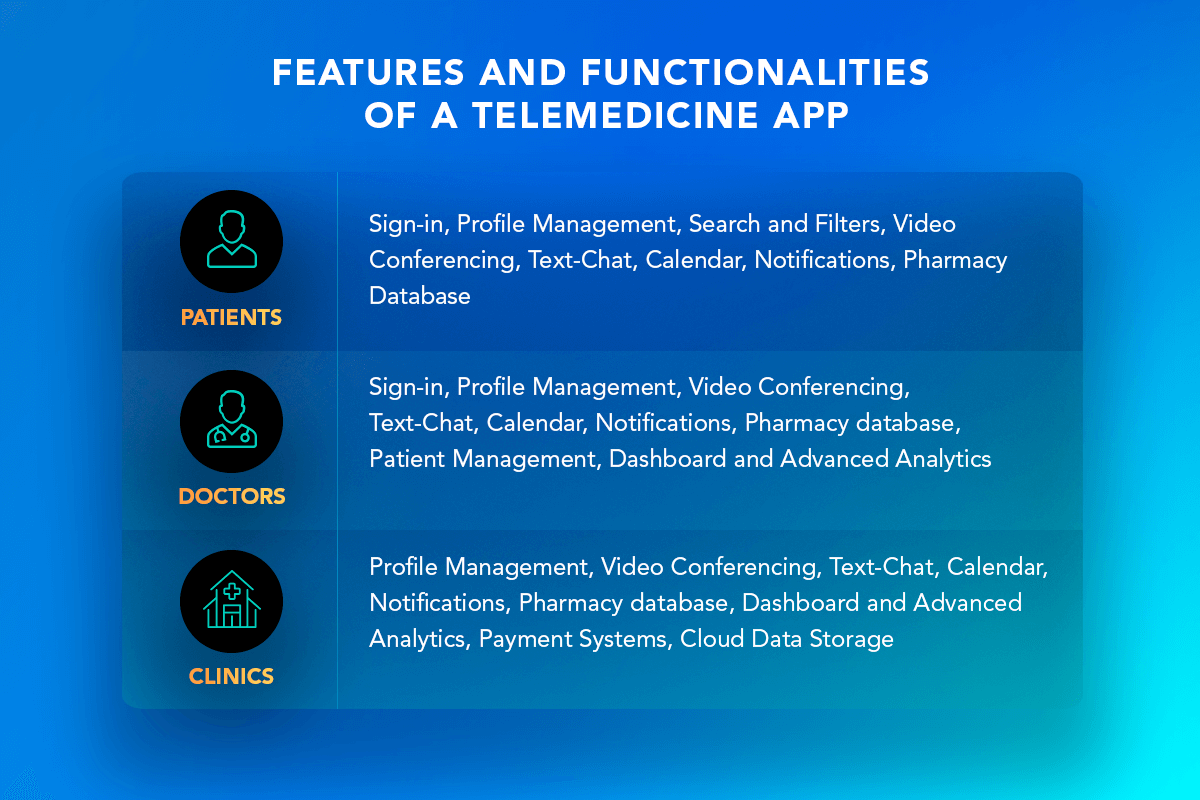
- Sign-in
The sign-in function allows users to add their accounts to the telemedicine platform. As a result, telemedicine apps store a lot of personal data, such as contact information, that must be properly secured. Patients can register themselves via email or with the help of third-party vendors, for instance, Google or Facebook. Two-step authentication using SMS or email is also available.
- Profile Management
After signing in, a user creates a personal account, which is intuitively managed by its owner and easily viewed by physicians. The profile owner solely decides which information to share or keep private.
- Search with Filters
As the telemedicine app development mostly offers a vast spectrum of services and doctors for consultations, advanced search functions help the users to navigate the platform easily. To find the most suitable option, a patient can apply various filters, such as medical specialty, gender, and language.
- Calendar Management
The in-app calendar enables users to manage appointments better. Patients can view available time in doctors’ calendars, make appointments and reschedule meetings. Surely, before any changes are applied, they need to be approved by the chosen medical worker. Moreover, the telemedicine app calendar can be synced with Google Calendars.
- Video Meetings
Scheduling meetings allows users to communicate virtually using cameras. Telemedicine meetings can be patient-to-doctors to obtain medical care and doctors-to-doctors for professional advice. Video communication allows getting needed help in real time without leaving a convenient location.
- Text Chat
The chat function allows patients to approach doctors via text messages rather than by scheduling virtual doctor visits. One-to-one texting can be an effective way for ongoing communication. Text messages are well suited for cases when a patient needs advice about drugs or changes in nutrition. Moreover, users can exchange images and documents, such as lab results, X-rays, etc.
- Notifications
A doctor on-demand app will send users notifications, reminding them about appointments or informing them about occurring changes. Additionally, doctors can be notified about the emergency state of their patients.
- Payment System
A telemedicine app can use various payment models. Be it a freemium pattern, a subscription model, or a fee approach, app owners can effectively monetize offered services, reducing the cost of real-life consultations.
Payment Models of Doctor-on-Demand Apps
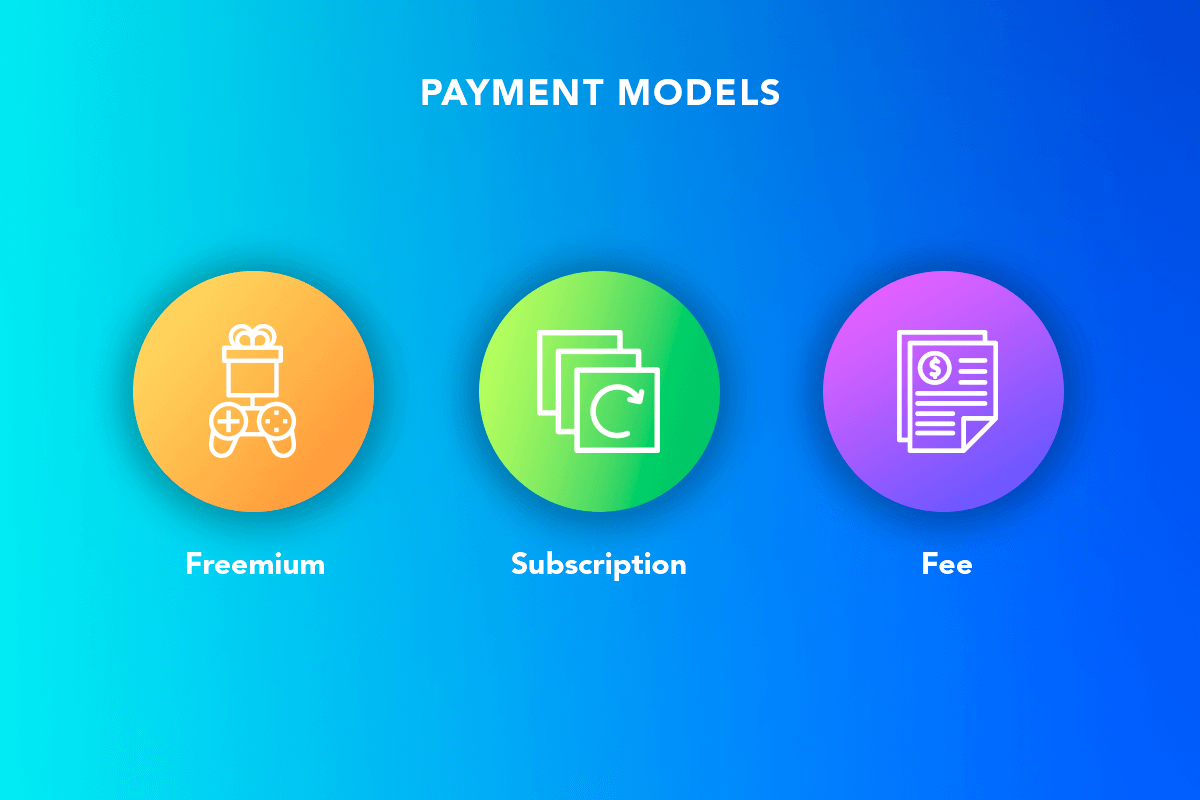
Freemium is a type of pricing model that offers customers both complementary and extra-cost services. An app provides basic services for free for the user to try. However, offering more advanced services or additional features at a premium.
The subscription-based approach is a business model that charges users a recurring fee — monthly or yearly — to access a platform’s services.
The fee business model refers to a fee charged for a particular service, for instance, paying for one performed medical consultation.
- Pharmacy Database
A telemedicine app contains a wide pharmacy database, which is regularly updated. The doctor on-demand app allows users to contact directly with drug stores so that they can receive current information regarding the availability of necessary medicines.
- Cloud Data Storage
With Cloud-powered data storage, owners can store all data securely in the cloud, making them sharable and easily accessible across various devices.
- Dashboards and Advanced Analytics
Telemedicine apps can provide real-time data analysis based on numerous internal and external sources. The extracted information is then visualized interactively through charts, diagrams, and graphics.
Read more about Data Analysis in the Medical Context.
Development of a Telemedicine App
A telemedicine app requires three main components: a camera, a microphone, and custom software. The doctor-on-demand software connects users by providing them with the needed tools to ensure communication. A camera is applied for video conferencing, and a microphone is used for audio exchange.
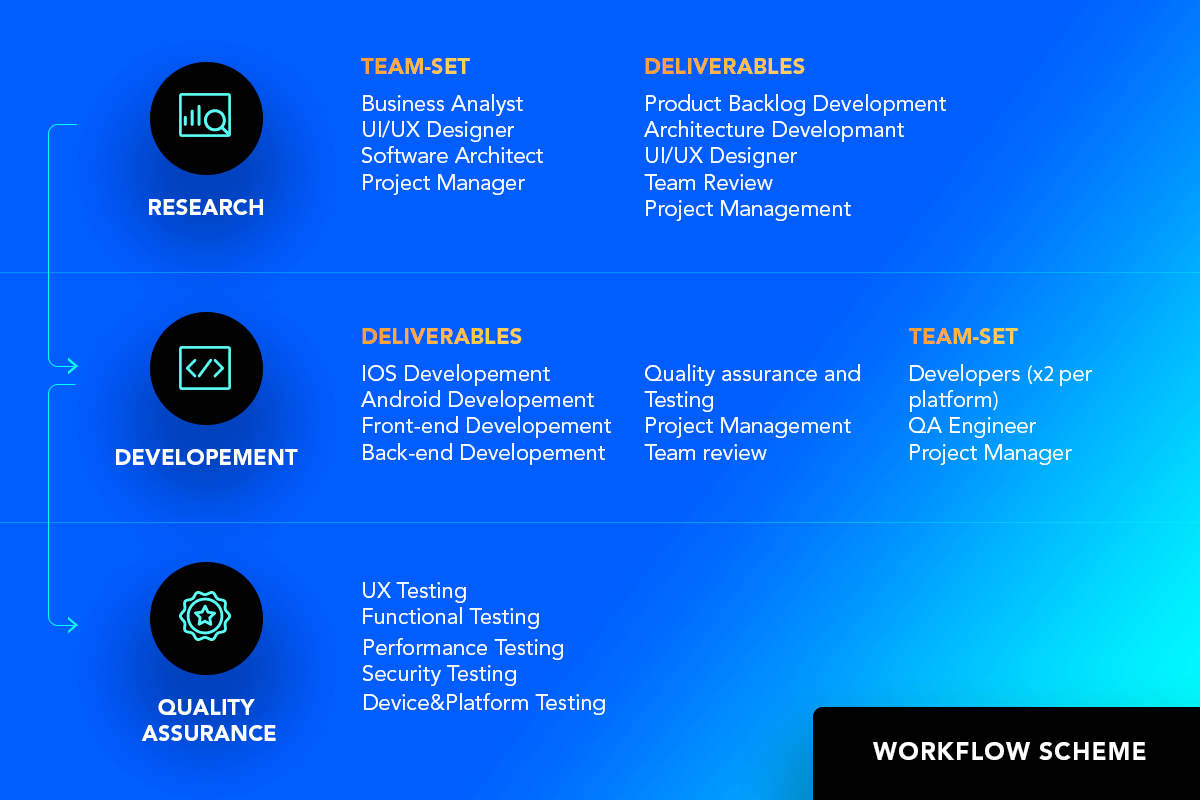
Telemedicine app development can be divided into three main phases: research, development, and quality assurance. These stages are typical for any software development. However, telemedicine software has its specificities.
Research Stage
The research stage includes a business analysis of the market and the main competitors. It is at this stage that the target audience, app objectives, project plan, and budget are to be defined. Based on the project goals, the development team plans the software architecture, UI/UX design, front-end, and back-end development.
Development Stage
This stage covers the actual working out and coding of a telemedicine app. The development stage includes various processes, such as establishing the development environment, writing various parts of the code, and preliminary testing of the app.
Quality Assurance Stage
The QA stage aims to ensure the high-end quality of the final version of a telemedicine app. The QA testing helps to make applications stable, usable, and secure. This stage covers UX testing, functional testing, performance testing, security testing, and device&platform testing.
Read more about UX design.
Examples of Telemedicine Apps: Uber for Medical Services by Softengi
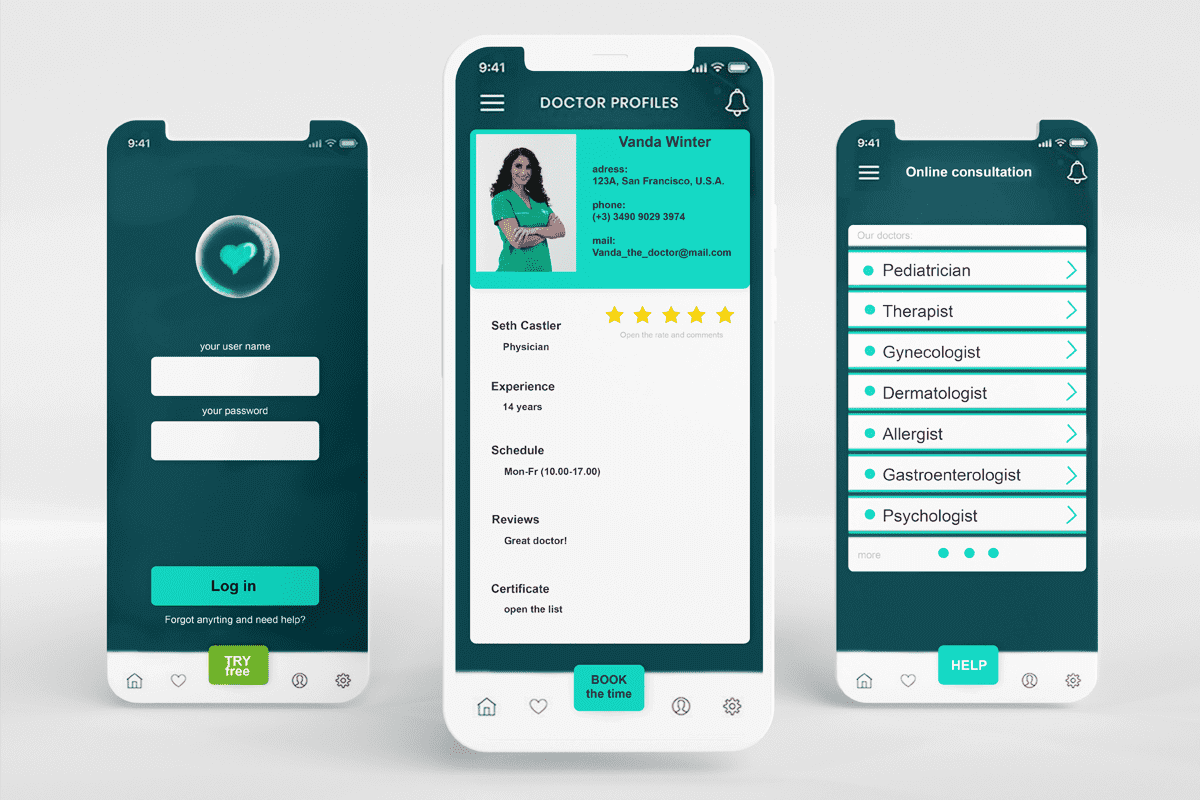
Softengi has developed “Uber for medical services” – an advanced telemedicine app providing a database for specialists. Telemedicine consultations are carried out by transmitting medical information through secure telecommunication channels. The information includes the patient’s history and special medical data that specialists can collect and transfer from the patient’s house to a remote telemedicine center for further processing. By applying various filters, users can easily find a needed medical professional and get an online video or audio consultation.
Read more about Uber for Medical Services
Doxy me
Doxy me is a telehealth solution used by over 500,000 health professionals. The app is designed to host appointments virtually, providing a peer-to-peer video platform to match patients with health professionals. The company claims that it hosts about 250,000 video sessions a month. The solution is HIPAA-compliant and offers secure video conferencing features.
Babylon Health
Babylon Health offers a telemedicine app that supports remote consultations with doctors and health care professionals via text and video messaging. According to Forbes, Babylon Health digital healthcare app is valued at $2 billion. AI-powered, the Babylon solution offers a mobile consultation service providing real-time appointment booking.
Our AI has been designed around doctor’s brain to provide accessible healthcare for millions in the palm of their hands. It can understand and recognize the unique way that humans express their symptoms. Using this knowledge, combined with a patient’s medical history and current symptoms, it provides information on possible medical conditions and common treatments.
Babylon Health
Conclusion
As the coronavirus spreads, telemedicine app development, with its ability to provide remote medical collaboration, attracts much attention. An alternative to traditional medicine, a telemedicine app allows patients to get needed consultations with chosen doctors virtually via video or audio conferencing. Furthermore, top-notch technologies such as Artificial Intelligence and the Internet of Things extend the capabilities of telemedicine software, making it smarter and more helpful to its users. With its restrictions compared to in-person visits, telemedicine cannot replace traditional healthcare services. Nevertheless, Softengi believes in successfully converging traditional medicine and telehealth innovations.






