EHS management is undergoing a transformation with the influence of modern technologies: Virtual Reality, Machine Learning, Computer Vision, and others. This article will focus on Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in EHS. Specifically, we’ll discuss the following topics:
- AR/VR in times of social distancing;
- AR/VR for a safer workplace: onboarding training, safety training, remote assistance;
- Emergency response. Strengthening the capacities with virtual reality;
- Virtual life-saving tools for medical use: VR medical training, VR for pain relief, AR for interventional procedures.
Also, we’ll share an insight into the future of such technologies. Let’s go!
AR/VR for Social Distancing: Products and Practices
Use areas of VR/AR are vast, mainly due to the restricted live interactions caused by COVID. The pandemic brought many changes, and the technological world could offer the best response to the new needs. So COVID-19 served as a driver for digitalization. Communication has assumed even greater importance during the pandemic. Even after the vaccine is widely adopted, many companies will allow their employees to continue working remotely. According to a Gartner survey, 90% of HR leaders plan to allow employees to work at least part of the time remotely.
Remote work means permanent changes to the way companies approach workplace safety. For instance, there is a high chance that future meetings will be held in virtual reality as it minimizes health risks and preserves the effect of “presence.” It isn’t easy to believe in it right now, but who knew we would be having Zoom meetings instead of personal talks ten years ago?
We’ve already witnessed companies grappling with the pandemic challenges in 2020, but this year pushed safety professionals to rethink their practices and explore new opportunities for connection and collaboration.
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality can accomplish it by simulating those environments for workers to practice in. Overall spending on AR and VR rose in 2020 to US$12 billion globally, up 50% from 2019. And it continues to rise.
However, don’t get things wrong. VR won’t be over together with the pandemic. The unexpected coronavirus pandemic has turned the working world upside down overnight: Remote work has become the new reality for many employees across industries. Many experts agree that the overall acceleration of digitalization during this time will have a long-lasting impact on occupational safety. Safety training and education are considered to benefit most directly from this development.
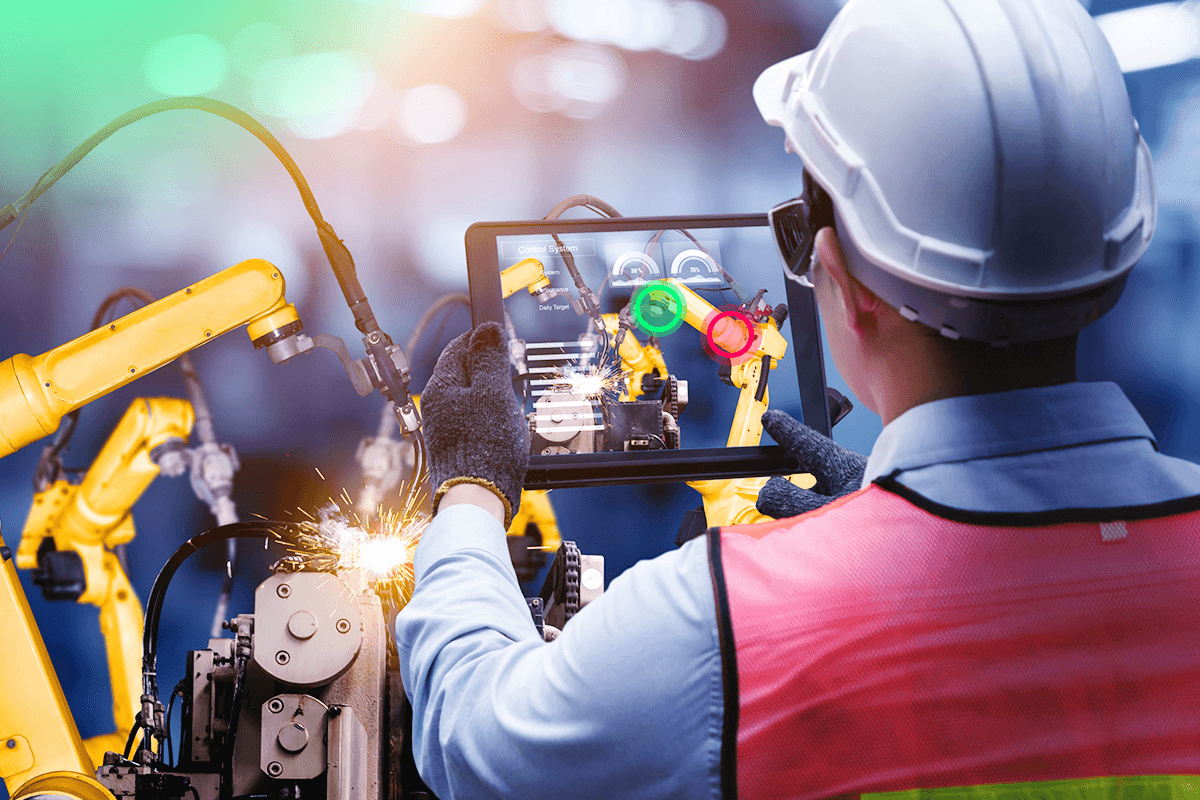

Safety risk is a real challenge across nearly every industry. Whether it’s frontline retail employees exposed to robbery incidents, manufacturing workers operating potentially dangerous machinery, or hazard identification in the field, workforces face risk. To minimize liability issues and protect people, every organization stands to gain from going beyond traditional types of training.
Using these technologies allows employers to improve safety outcomes, increase preparedness, and boost employee performance while significantly reducing costs. Scalability, effectiveness, and improved safety outcomes are some of the reasons why VR can have a future. Some experts predict the industry will reach a total of US$73 billion in 2024.
AR/VR Training for EHS
VR training brings benefits to almost all business areas. EHS is not an exception. Training is vital for preventing incidents and keeping your working environment safe and productive.
Standard training procedures may no longer be possible. COVID-19 has forced companies to review, rethink and reimagine employee onboarding and training systematically. Virtual learning offers a chance for companies to create standardized documents and videos to ensure all employees have a baseline knowledge of proper safety protocols.
VR/AR technology can support just-in-time learning to teach employees in a more flexible, on-demand, and accessible format. The technology enables gamification to create engaging, immersive, and potentially more memorable learning experiences than listening to hours of lectures or reading pages of materials. That is why AR/VR technologies can improve and even enhance our training experiences in any environment.
VR Safety Training and Remote Assistance
The pandemic makes it impossible to teach and learn in person about unloading hazardous materials, configuring a wind turbine, or maintaining nuclear power plants or oil platforms.
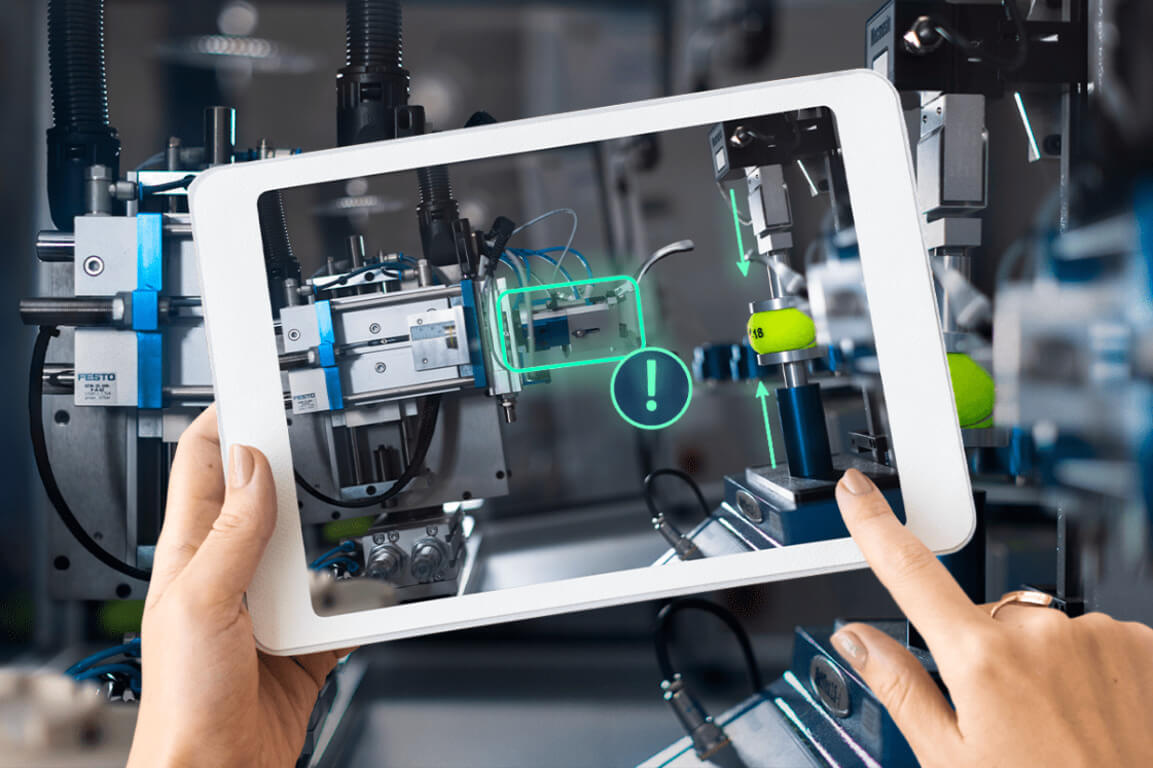
Using virtual reality is a great way to show employees how to work remotely in volatile and risky conditions. For instance, it is possible to recreate the oil platform’s 100% accurate environment and train future employees using VR instead of a physical facility. Such representations are called digital twins. AR-based virtual user manuals provide details on a vehicle dashboard or give workers insights into the factory machinery.
It is also possible to use augmented reality for remote assistance of specialists. For instance, if maintenance or fixing is required and specialists have to work remotely, they can use AR apps for creating visual guidelines.
Emergency Response and Risky Environments Made Safer with VR Training
AR/VR allows engaging specialists remotely from all over the globe, especially when particular knowledge is required. It is vital for specific industries and unique experience sharing. For some, this experience may be life-saving. Here we can name not only emergencies or cases of imminent danger but also medical treatments. It is easily achievable with AR/VR.
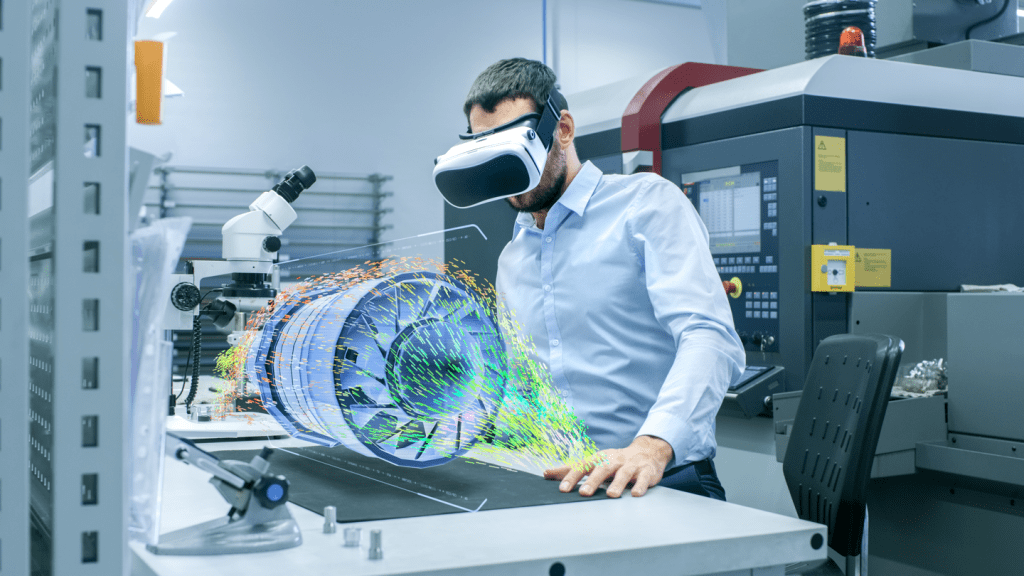

Virtual/Augmented reality allows employees to learn without putting them in potentially unsafe situations, for example, during a firefighting simulation. Such solutions are ideally designed to help in emergencies and post-emergencies. The training scenarios are carried out in a safe environment but create an authentic feeling.
Ensuring effective and accessible safety training for environments where inadequate safety procedures and low awareness pose a huge risk to employees is critical. Such environments include:
- Industrial assembly lines;
- Quick-service restaurants;
- Frontline utility work;
- Oil & gas platforms.
VR can be used to train employees in a safer environment and give them an immersive learning experience. For example, emergency training in dangerous situations or to train and boost the level of emergency preparedness.
To sum up, VR is safer and less risky for employees. With VR, people do not need to travel to access training devices, and they do not need to bring heavy equipment to a special training location.
AR/VR in Healthcare: Training, Telemedicine, and More
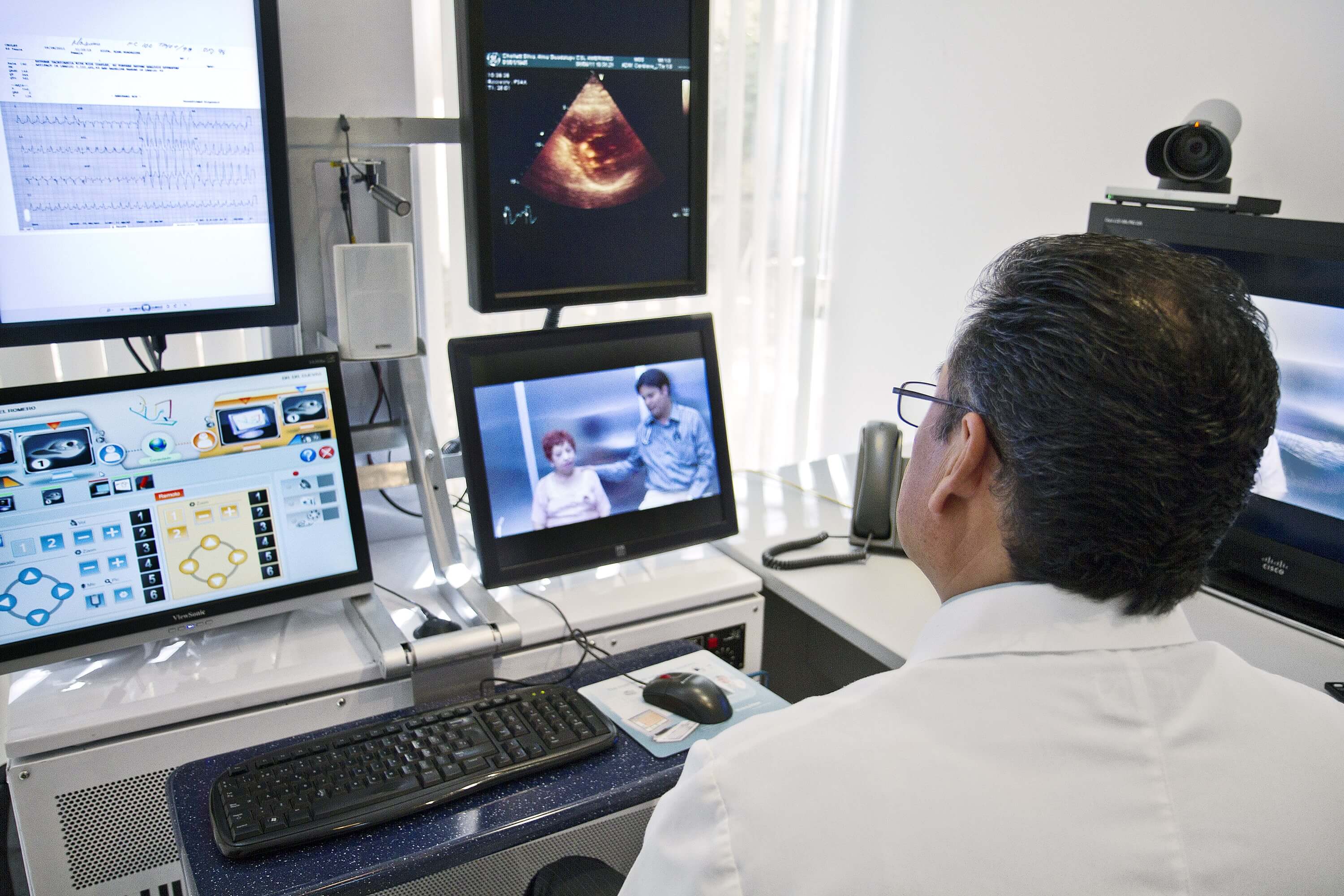
Virtual Reality solutions are overall changing the way we think about medicine. AR and VR in healthcare are gaining momentum due to widespread adoption in telemedicine, medical training & education, patient care management, and medical marketing during the COVID-19 pandemic.
To learn more about telemedicine and its effectiveness, we recommend reading our case study below.
VR and AR are increasingly adopted in surgeries, diagnostics, and rehabilitation. Ultimately, these technologies create a positive impact on our well-being. VR in medical training helps doctors learn how to conduct complex operations without any patient risk. Systems such as touch surgery use virtual reality to view the patient’s anatomy and physiology, thereby assisting doctors in the operating room.
For example, Imperial College and St. Mary’s Hospital in London use Augmented Reality glasses to visualize 3D imaging of blood vessels during reconstructive surgeries. This way, AR technology helps with getting a better surgery outcome.
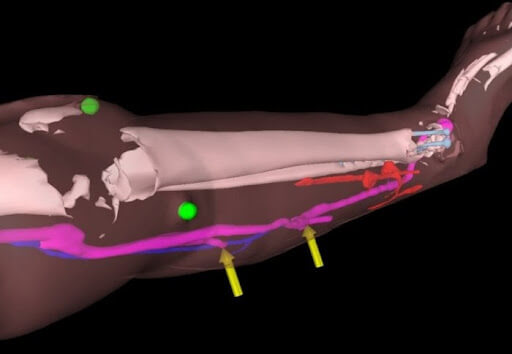
Source: Imperial College
Additionally, AR is being widely adopted for education and training purposes for medical personnel. Since AR-based learning modules provide anatomical visualization and simulation, it gives the medical personnel a complete learning experience.
Apart from training, VR technologies are used in telemedicine to improve communication between patients and doctors by providing a more immersive experience. An advanced VR-powered interface enhances the user experience and allows exchanging medical data more accurately.