Whether you call it the 4th Industrial Revolution, Industry 4.0, or Smart Industry, the message is pretty much the same – all industries go digital. Full automation is no longer a fantasy. It is our true reality. Logistics, manufacturing, automotive, retail, oil & gas, pharma, medicine, etc., companies can start the process of digitalization step by step just using the visual data they have accumulated. They all have cameras, after all.
One prominent industrial technology that has been gaining a lot of traction recently is Machine Vision. It helps to deliver superhuman capabilities to the processes that required lots of time and effort from hundreds of employees earlier! To answer the question that you might have, “No, it doesn’t cost much because of the progress in this sphere!”
Just a few use cases where computer vision for quality control has already paid off:
- Using computer vision to assess medical images ( count bacteria on them, determine the presence of any virus);
- Applying computer vision to determine counterfeit goods during the packaging process;
- Applying machine vision to find cars in forbidden areas;
- Using computer vision for quality control of pests in agriculture;
- Applying computer vision for maintaining a security perimeter;
- Using computer vision for PPE enforcement;
- Applying AI to control the goods on the shelves of the supermarket.
Any repetitive control process from any business sphere which requires human actions can be automated today! And companies that do it see tangible benefits really soon in terms of money and working hours. One important idea before you start reading: each AI-powered system for quality control provides more and more accurate results ( in our last project, we’ve managed to reach 99% accuracy ) with more data fed into it. In contrast to humans who only get more exhausted and inattentive.
AI Business Case 2021
Computer Vision or Machine Vision?
Today, Computer Vision and Machine Vision are recognized as belonging to the range of the most prominent modern technologies. Although the boundaries between them are often blurred, they are not the same.
Computer Vision, often abbreviated as CV, is a broad technological field that concentrates on the analysis of images or sequences of images to extract information. It includes image recognition, video recognition, optical character recognition, and computer algorithms to understand the content of digital images.
Conversely, Machine Vision is used to perform performing narrowly defined tasks such as object counting or defect searching, while CV can be used for more complex tasks in a wide range of fields, primarily in industrial applications.
How Does Machine Vision Work?
Machine vision systems acquire images of objects, process them, and then analyze the output, measuring diverse characteristics undetected by the human eye. A combination of Machine Learning techniques and smart image processing approaches allows to identify and distinguish between objects without human intervention.
Machine Vision for Quality Control
Machine Vision stands behind many great advances in industrial automation. One of the most prominent achievements is the field of quality control.
In a lot of companies, quality control is still a manual operation. However, although the human ability to visually inspect different objects is very high, subjectivity and fatigue resulting from performing repetitive tasks may result in human errors. By contrast, CV-based automated systems offer an effective solution for quality and process control, adding value to inspection operations due to enhanced productivity, the accuracy of the manufacturing processes, and the reduction of operational costs.

A CV-based automated system includes a camera looking at a production line that captures images which are then algorithmically compared to a predefined image to detect defective objects. The application has found major adoption for the detection of imperfections, geometric inspection, packaging control, product classification, surface finish inspection, color and texture analysis, etc.
Benefits of Computer Vision for Quality Control You Can’t Deny
Accuracy
CV-based approaches ensure a higher grade of accuracy within the accepted tolerance in every manufacturing process. Even when workers use specific equipment, such as a magnifying glass, machines are still more precise. For example, it’s possible to improve the level of bacteria detection for medical equipment by 95%, as we did in this case.
Repeatability
When it comes to repetitive work, CV-driven systems conduct monotonous tasks more effectively. Implementation of a fully automated system definitely speeds up the production time as the machine needs no time for thinking and, compared to an employee, its accuracy and repeatability are far greater.
Reduced Downtime
An automated system is an effective tool to reduce quality control downtime. As the system is fully automated, it runs much faster, can work 24/7, and does not need any breaks for rest.

Reduced Costs
An automatic machine vision system provides tangible economic benefits. With such a system, manufacturing companies do not require working personnel to manually perform control of manufactured products, allowing them to concentrate on more important work. Additionally, a CV-powered system does not make mistakes, which can appear during manual control. The cost of a small human mistake can sometimes be valued at millions if not billions of dollars, and Machine Vision helps to avoid it.
Computer Vision for Quality Control Use Cases: Product Manufacturing
Commercially adopted automated visual check of products and their packages powered by Computer Vision technologies is becoming increasingly popular.
As customers unconsciously associate the appearance of a product with its quality, manufacturers are getting increasingly concerned with how products look. Automated visual systems significantly contribute to packaging and product inspection, identifying defects, functional flaws, or contaminants faster without human involvement.
One of the many industries that are making active use of Machine Vision is the pharmaceutical industry. As a result of implementing CV-based systems, pharma companies are ensured that each unit of their produce meets relevant quality requirements.
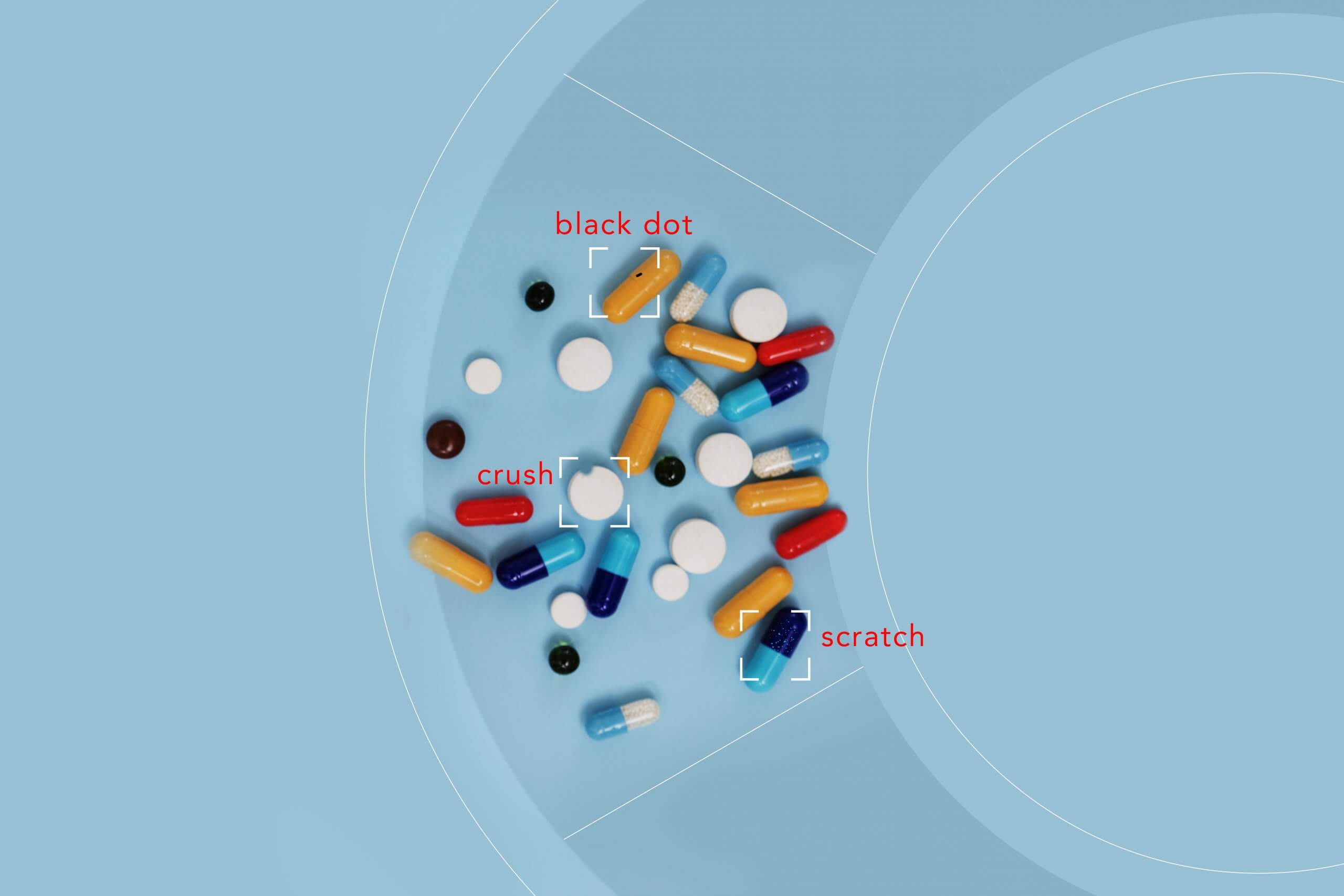
Machine Vision software can count tablets and capsules before packaging them, inspecting each pill for accurate shape, size, and any defect, identifying damages in packages, and even validating their labeling. In addition, such a system can be programmed to temporarily stop the production line if a mistake is detected. Package and product inspection with Computer Vision technology helps manufacturers to reduce quality control costs and enhance efficiency.
Computer Vision for Quality Sorting
The ability of Machine Vision to distinguish between different characteristics of products makes it a useful tool for object classification and quality evaluation. Machine Vision applications can sort and grade materials by different features, such as size, shape, color, and texture, so the losses incurred during harvesting, production, and marketing can be minimized.
This system has found its use not only in manufacturing processes but also for inspection of incoming materials and resources needed for production. For instance, A visual system in the food industry can objectively determine the quality of food and agricultural products. This application easily identifies blemishes in vegetables and fruits, as well as insect infestation in grains.

Implementing this CV-based application helps production companies to select high-quality materials for their needs, meeting all manufacturing requirements.
Computer Vision for Defect Reduction
A highly sensitive automated defect classification powered by CV technology can contribute a lot to reducing production defects.
In case a CV-driven system finds a defect, it identifies its type and classifies the product according to its type, and assigns it a relevant grade. The damaged product can be removed or altered before it adds further value in the next stage of manufacture.
Final Word
In terms of digitalization, Machine Vision is rightly considered one of the most prominent technologies. Applied in many different fields, Machine Vision adds value to quality control processes, making them fully automated and thus more productive and cost-effective.
In the field of Q&C, the main applications of this technology are automated sorting, counting, inspection, and packaging. CV-based applications serve to minimize human intervention, optimize operational efficiency, as well as reduce labor costs. Enabling objective non-contact evaluation, Machine Vision inspections are especially well suited in the industrial context.






