Over the last few years, emerging technologies are accelerating the pace of disruption in many industries. As the world market becomes more dynamic, major brands such as Ford and Jaguar start looking for more digitalized and consumer-focused business models. As experts in developing XR apps for automotive companies, we’d like to share some of the most prominent cases of the industry.
XR in the Automotive Industry: Case Study
Extended Reality: AR, VR, and MR
Extended Reality is an umbrella term, which envisages an artificially created environment, that combines the real and virtual worlds. The term covers virtual, augmented, and mixed realities, which differ in the degree of the user’s immersion.
Augmented Reality (AR) is overlaying certain digital content on the existing reality, thus allowing users to get partially immersed into the virtual world.
In contrast to AR, Virtual Reality (VR) ensures total visionary and sensory immersion replaces the real environment within the artificial one.
In Mixed Reality (MR), the users interact with a new environment created by merging real and virtual worlds.
Extended Reality Automotive
Extended Reality technologies gain traction across all industries. According to Statista, in 2021 the global AR-VR-MR market was estimated to be 30.7 billion U.S. dollars and is expected to hit 296.9 billion U.S. dollars by 2024.
In the fast-paced automotive world, companies experience huge pressure from permanently emerging revolutionary innovations. To stay ahead and be able to create the cars of tomorrow, vehicle producers have not only to keep track of the new market trends but anticipate and foresee them.
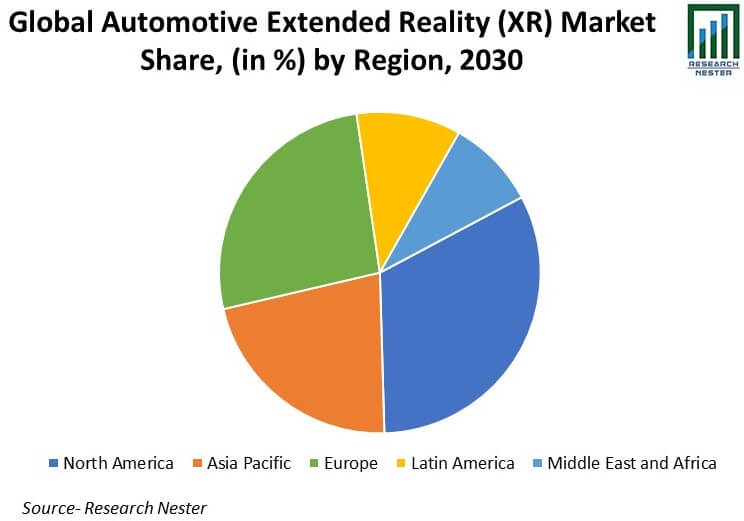
According to Research Nester, North America will be the biggest Automotive XR market in 2030. Asia-Pacific and Europe won’t be far behind.
Availability of Immersive Experience
Global technological advancement is opening the whole potential of the Extended Reality automotive technologies, and the relative affordability of hardware and development frameworks unleashes multiple opportunities for XR adoption both for car giants and local dealers.
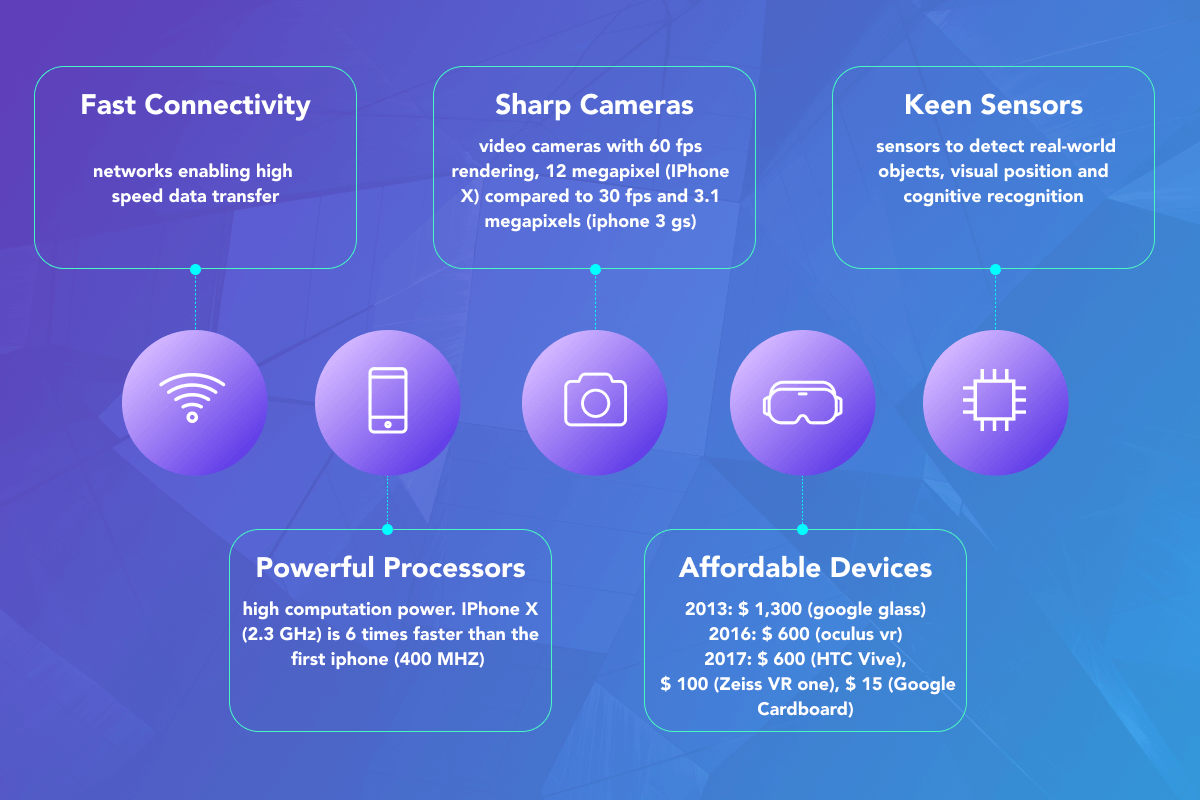
Fast Internet connectivity enabled due to the adoption of 4G and 5G networks has made the processing power much higher than ever before. Technological progress becomes clearly evident, even from a consumer perspective. Just compare the characteristics of the video camera of iPhone 3GS and X, which are 60 fps rendering, 12 megapixels in iPhone X and only 30 fps rendering, 3.2 megapixels in iPhone 3GS. Mass adoption of XR applications across many industries is accounted not exclusively for by their ability to ensure higher quality but also because AR and VR devices are becoming less and less expensive.
With the appearance of smart sensors, the detection of objects in real time, visual positioning, and cognitive recognition are being implemented more and more effectively. Due to matured sensor systems, IoT technologies (Internet of Things) are spreading very fast, at the same time facilitating the need for faster, more intuitive interaction and visualization.
How Extended Reality Automotive Technologies Impact Companies?
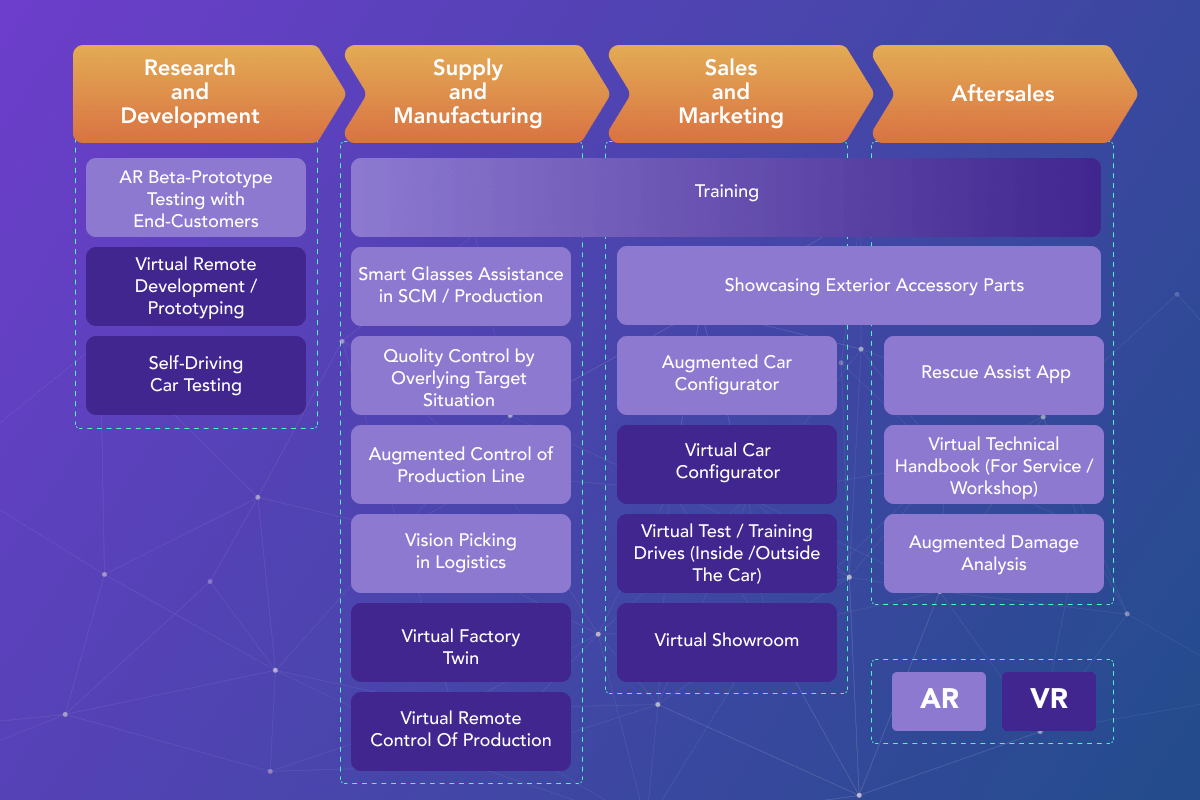
VR and AR applications have transformed the entire value chain, from R&D to manufacturing, marketing, and aftersales, as well as the product itself.
Many major automotive supply chains implement AR and VR technologies as part of their R&D and design processes. Among the most effective applications of XR are prototype testing by the end customer, VR remote development, and VR-powered self-driving car tests.
Also, XR finds its use in the manufacturing and supply field. With the ability of AR and VR to represent complex assets and investigate the mechanical effects of clashes, the automotive industry effectively utilizes limitless possibilities of XR in practice. Some of the applications are AR training, smart glasses assistance in SCM and production, AR-embedded quality control, augmented control of production line, AR-powered vision picking in logistics, virtual factory twins, as well as virtual remote control of production.
In the wake of widespread digitalization, the market of the automotive industry is becoming more consumer-focused. Automotive companies seek to create more personalized marketing models to satisfy their audiences. By applying Extended Reality Automotive solutions, car producers now offer to their customers augmented and virtual car configurators, showcasing, virtual test-driving, and virtual showrooms.
XR is used not only while interacting with customers. The technology is implemented in production as well.
Read our article about using XR for remote production.
XR-powered solutions are also penetrating the delivery of aftersales services. Among the main use cases are rescued assist apps, virtual technical handbooks, and augmented damage analysis.
The Most Prominent Use Cases in the Automotive Industry
The industry utilizes XR technologies in several major fields:
- Virtual prototyping
- Augmented training
- Immersive showrooming
Let’s take a closer look at them.
Virtual Prototyping
Today, customers are looking for more fuel-efficient, greener, safer, and secure cars. In order to meet customer demands, automotive companies have turned to more innovative approaches. Implementing VR-powered prototyping automotive solutions can help car producers better simulate vehicles in terms of volume, size, and distance. Using VR embedding, engineers can directly interact with the virtual prototype of a vehicle and get a better view of all its systems, which enables them to detect conception errors at an earlier stage. Virtual Prototyping allows automotive engineers to correct errors in real time directly on the prototype, which helps accelerate development, improve productivity, reduce costs, and in the long run, deliver a better product.
Ford Motor Company has been applying VR-based technologies at various stages of its development processes since 2000. Today, instead of creating expensive physical models, Ford makes active use of VR for car design by utilizing VR headsets.
“What we’re looking for is the perceived quality of vehicles, as a customer would see them,” Elizabeth Baron, virtual reality and advanced visualization technical specialist at the company, says Forbes. “We want to be able to see the cars and our designs and experience them before we have actually produced them.”
Augmented Training
AR has found its use in the transformation of training processes, making them more efficient and automated. Using an AR device, automotive companies can replicate any possible real-life situation without any risks that might occur in real life. By using such devices as AR glasses, headsets, or tablets, AR training solutions enable employees to see in real time step-by-step processes and procedures.
If you want to know more, read our article about workforce training in VR.
Jaguar Land Rover (JLR) has successfully introduced AR technology into their training programs, allowing them to educate trainees without having to reinstall or remove the dashboard of Jaguar’s vehicles. Using AR applications, employees can visualize on a tablet JLR internal data with individual components viewed from different angles. This solution helped the company reduce costs, enhance efficiency and improve the quality of JLR vehicles.
Immersive Showrooming
Today, VR and AR technologies are rapidly transforming the way vehicles are sold in the automotive retail industry, at the same time enhancing the customer experience. In the digital era, a customer does not need to visit a car dealership in order to buy a car. Innovative digital showrooms make car purchasing more accessible and engaging for customers, as well as easier and cheaper for car retailers.
According to V12 Data’s research, when buying a car, 70% of the younger generation see emerging technologies and infotainment features as extremely useful.
In a virtual reality showroom, customers can sit on a chair, which feels like a real car seat, and, by using a VR headset, get a real-time experience of the car in a 3D 360-degree virtual environment. Furthermore, a potential customer can browse through all possible equipment options and colors virtually, configuring the desired car’s features themselves. As test drives are offered in entirely virtual reality, they generate more audience, cut costs on auto transportation and allow companies to get wider first-hand feedback.
Audi dealership network has deployed functional VR applications for customer consultation. One of the smallest Audi dealerships in the United Kingdom, London Audi City showroom with a total area of only 420 sq m, by implementing a VR-embedded solution, provides its customers with a realistic experience of their individually configured vehicle, down to the last detail.
“With the VR experience, we have developed a full-fledged sales tool for Audi dealers. It offers our customers more information and certainty when making their purchasing decision, as well as a special excitement factor,” says Nils Wollny, Head of Digital Business Strategy/Customer Experience at AUDI AG. “With this, we are taking the next step in our strategy to combine digital innovation with the strengths of the bricks-and-mortar dealership.”
Other Extended Reality Automotive Applications and Use Cases
Holographic AR Navigation Systems
South Korean auto giant Hyundai Motor, which has long been associated with innovations, has also applied AR and VR technologies in its business. Recently Hyundai has introduced its AR navigation system equipped on Genesis G80.

The system provides drivers with guidance hints, destination points, navigational information, as well as holographic image alerts on the windshield that are perceived as part of the road.
AR Manuals
Mercedes-Benz deploys AR technology to help its customers better understand car devices. The AR manual offers users a step-by-step virtual guide, which helps to reduce many complexities. With Ask Mercedes, an AR app of Mercedez-Benz, users can scan a machine or specific controls and displays within a vehicle, identifying all embedded features.
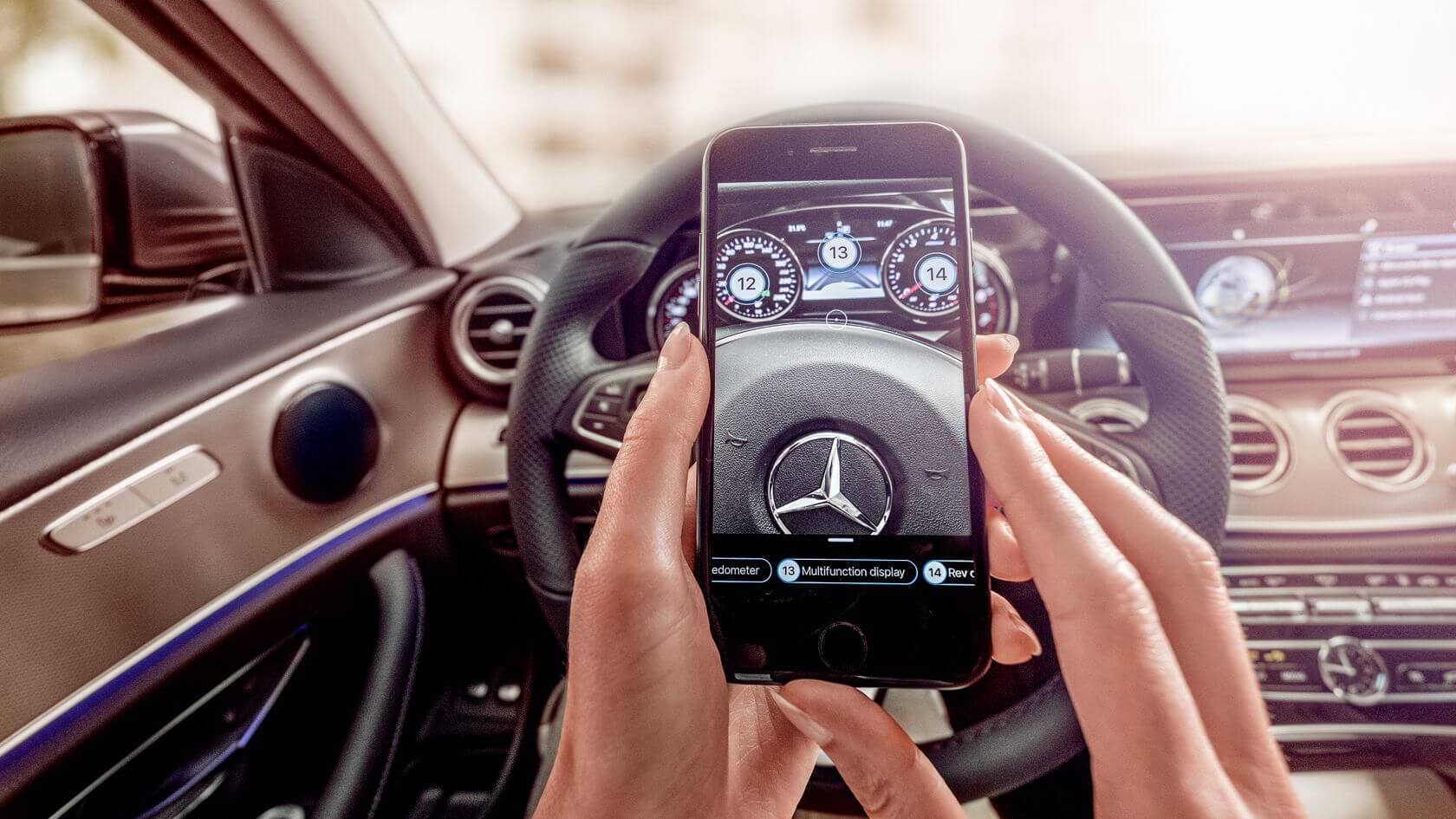

This solution allows Mercedes consumers to avoid long text descriptions and how-to videos.
Planning of Production Plants
The BMW Group Production has been focusing on extended reality for a long time. By implementing XR, BMW enabled assembly planners to assess the whole production in a virtual environment, as well as test new processes in 3D.
Matthias Schindler, responsible for Virtual Planning and Implementation in Production at the BMW Group, said: “Virtual reality technology has enabled us to set up cockpit workstations quickly and efficiently. Time-consuming trial installations that replicate the workstation in its actual dimensions were no longer needed. And the fact that all the specialists involved – from logistics experts to systems planners to production employees – were easily able to exchange ideas in the early stages was an important added benefit for the team. We were more transparent, more flexible, and faster overall.”
Conclusion
From prototyping to manuals, world-known car brands use XR technologies to optimize their workflows and improve customer experience. There is one more aspect we’d like to highlight – security. Creating VR simulations, one of our services, allows engineers to see how the car will behave in real situations with regard to static and dynamic obstacles.
Digital car showrooms, another of our XR services, are a part of the global trend – retail gamification. Engaging customers with XR technologies allows car dealers and retailers across other industries to smooth out the impact of COVID-19 restrictions and increase sales. More facts about gamification in retail here.






