«I am excited about Augmented Reality because unlike Virtual Reality, which closes the world out, AR allows individuals to be present in the world but hopefully allows an improvement on what’s happening presently.»
Tim Cook, Apple CEO
Today utility and energy sector is facing a massive wave of powerful disruption due to the advance of progressive IT technologies. The increasing demand for electricity in rapidly developing countries and growing cost pressure make this industry reconsider the traditional business models it uses. Augmented and virtual realities are on the way to innovate and reshape this sector. According to ABI Research, by 2022, total AR global market revenues for the energy and utility sector will reach US$18 billion. What will this money will be spent on? I am going to give the answer to this question later. First things first.
What Is the Difference Between AR & VR?
One of the most innovative technologies responsible for current tech disruption is Virtual Reality (VR). By simulating an alternative reality, VR technology allows immersing the user in an artificially created environment, enabling his/her interaction with the virtual world. VR applications usually require specific devices, like a head-mounted display (HMD) and haptic controllers, which allow users to experience the imaginary world and manipulate virtual objects.
Augmented Reality (AR) refers to a real-world environment, which is complemented and augmented with different digital objects, like sounds, videos, and graphics overlaid over the physical environment. Unlike VR headsets, AR equipment does not block the view of the real environment as VR helmets do. AR is mostly applied in smartphones and smart glasses and does not require any additional equipment like helmets.
The main difference between AR and VR is that AR augments reality with software embedded in various equipment pieces. While VR devices provide an artificially created environment, AR devices complement reality enabling the user to manipulate, move and perform operational processes without obstacles in the real world.

What Challenges Can AR/VR Solve in the Utility Sector?
Today energy and utility industry is facing quite several challenges brought on by an aged infrastructure, the growing retirement rate of a highly qualified workforce, grid modernization, and governmental regulations. All these put big pressure on utility companies that want to stay competitive in the market.
There are two major problems that, nevertheless, are interconnected:
The most significant problem in the utility sector is the aging of the workforce, which leads to the loss of institutional knowledge. According to a report provided by the US Department of Energy, 25% of US employees in electric and natural gas utilities are going to retire during the next five years.
Therefore, companies are forced to fill open positions with novice workers whose professional knowledge and experience are limited. Additionally, utility companies face difficulty in finding a high-quality workforce. According to a survey by the U.S. Department of Energy, 72 percent of energy employers complain about the shortage of qualified staff.

Aging energy generation and distribution facilities is another significant challenge for the utility sector. Harris Williams & Co. estimated that nearly 70% of transformers are over 25 years old, while 60% of distribution poles are 30 to 50 years old. Under the existing circumstances, energy and utility companies are forced to upgrade their networks to provide reliable and cost-effective products for their clients.
Let’s see now how AR technology can help the utility industry overcome these challenges.
AR Applications for Energy and Utility Sectors
- Accelerated Asset Maintenance Process
One of the most promising AR applications is asset maintenance. AR technology can impose a 3D model on a piece of equipment in real-time, allowing for a certain range of problems to be solved faster and more efficiently. Field technicians equipped with AR mobile devices or smart glasses are empowered to immediately access operational documentation, revealing the asset type, maintenance history, or replacement conditions.
In case of any damaged equipment, this allows a lineman to react promptly by ordering a replacement or calling a technician to fix the problem. The introduction of AR applications into the energy and utility industry significantly accelerates operational processes, reduces costs, and saves time.
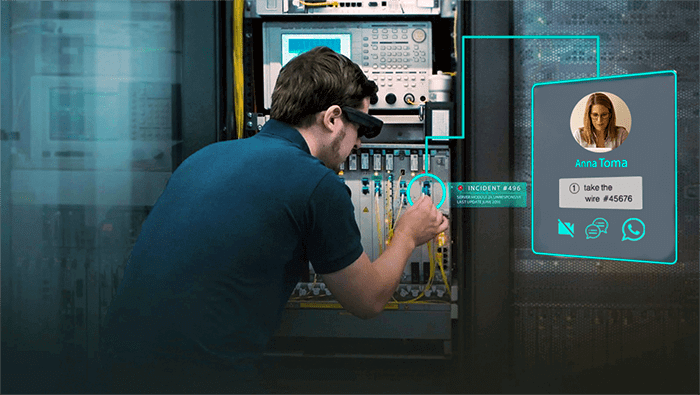
- Effective Remote Assistance
AR has also found its use in remote consulting. The technology allows company experts to guide inexperienced field workers in real-time, thereby significantly lowering expenses on subject matter experts (SME). When needed, using AR equipment, SME can guide junior workers, giving them eyes, ears, and hands on the ground. This application allows employers to keep in the workforce highly experienced retired or aging employees by providing them with the possibility to work remotely.
- Faster Specialists Training
One of the greatest opportunities VR/MR offers is employee training. Today any effective company has to educate its own workers in order to increase the efficiency of service delivery for customers. AR enhances learning processes by adding virtual objects, such as images and videos, to the surrounding environment. This allows utility employees to get anything they need right in their field of vision, enabling a better understanding of the equipment and operational processes. AR can help energy and utility companies significantly improve their training programs, as well as prepare a highly qualified workforce.
- Higher Operational Safety
AR contributes to improving operational safety. With AR equipment, employees are able to model underground assets and heavy equipment in order to forecast any potential problems.
Hazards of damaged equipment can be identified and taken care of due to the use of connected AR glasses which field technicians wear while performing their jobs. By using AR technology, safety protocol implementation can be visualized in real-time on the ground, improving productivity and work safety.

How Can AR Benefit Energy and Utility Companies?
1. Service Expenses Decrease
Using XR technologies gives companies a chance to hire experienced staff members and educate them using AR training programs. Furthermore, with XR solution, companies can avoid going through a complex diagnostics process of troubleshooting equipment, concentrating on fixing the AR-identified problems. Another area where AR can bring significant savings is the engineering workforce contraction.
2. Reduced Service Time
AR offers real-time availability of complex engineering knowledge and assistance of senior engineers, which will significantly cut off travel expenses and optimize the time required to complete a task. Besides, AR solution reduces the time required for completing fieldwork tasks as employees can easily access the information and statistics required.
3. Lower Accident Risk
By implementing XR technology, a company can detect systematic errors, thus reducing mistake probability. Regular and more efficient monitoring of the equipment helps to enhance safety in the workplace.
4. Less Training Expenses
XR approach to training employees is cheaper and more practical than conventional training models, as virtual training does not require expensive equipment.
5. Shorter Training Time
XR training is less time-consuming than traditional training courses. Besides, trainees can go through the training material at their own pace, making their learning more efficient. In addition, with XR technology, an energy and utility company can provide distance classes taught by leading coaches from all over the world.
XR-embedded technologies are coming into the energy and utility industry, providing better safety and efficiency. Investing in AR helps energy and utility companies to deal with quite a number of challenges, making business more effective and competitive. AR is no longer a futuristic concept but a reality. Its implementation in the energy and utility sector opens new possibilities for the development of this industry.





