“Electricity changed nearly everything about the way we live and work—and that scale of transformation is possible with the Internet of Things.” Ian Goldin, Director of Oxford Martin School, University of Oxford
The power industry is the groundwork of the industrial world, supplying commercial, industrial, manufacturing, and residential customers with essential energy. Being a continually growing industry, the electricity sector faces a significant challenge of coping with the ever-increasing demand for electrical power.
According to ReportLinker, energy consumption is predicted to grow worldwide by more than 40% over the next 25 years. In order to meet this challenge without raising prices for customers, the electrical power industry is looking for smart solutions.
The Internet of Things (IoT) opens a whole new smart reality to the utility industry, streamlining costs through optimizing operating inefficiency. According to McKinsey, the total IoT market size of about $900 million in 2015 is expected to hit $3.7 billion in 2020, growing at a CAGR of 32.6%.
Smart Home Solution Business Case from Softengi
Internet of Things in the Context of Revolution 4.0
Today, we are going through the fourth industrial revolution, which reshapes the way a lot of industries function. The First Industrial Revolution utilized stream and water power to mechanize production. The next one used electricity and assembly lines to create mass production. The Third Revolution came with computerization, paving the way for the IoT that is currently playing a major part in the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Abbreviated as IoT, The Internet of Things is a system of interconnected devices with actuation and potential programmability capabilities. In essence, an IoT-embedded system can connect different objects via networks, thereby enabling the collection of data from various devices that can be monitored and managed in real time.
The World Economic Forum in Davos this year paid a lot of attention to the IoT concept, describing it as a leading innovation to transformative change. «By focusing attention and coalescing support around tried-and-tested IoT solutions with clear societal and financial returns, the WEF’s Centre for the Fourth Industrial Revolution and its partners are committed to maximizing the value and impact of IoT investments.»

Challenges of the Electric Power Industry
The Electric Power Industry does not only struggle with growing energy demand, but it also faces such challenges as:
- Tough emission regulation;
- Growing reliability expectations;
- Aging infrastructure;
- Spread of distributed energy resources (DER);
- Retiring workforce;
- Frequent accidents.
All these factors combined stimulate companies to look for ways to run businesses more effectively by using lean operations to create value for their stakeholders. One of the solutions that can make it possible lies in the modernization of grid infrastructure.
What Can IoT Offer to the Electric Power Industry?
IoT is key to most problem areas in this industry. IoT includes three core elements that make this technology so prominent: asset digitalization, asset data collection, and computational algorithms to manage the network created by interconnected assets.
All these components can enhance the efficiency and performance of the electric power grid at three levels: obtaining data from different sensors enhances the resilience of the grid, thus allowing power companies to manage resources more efficiently based on the information collected from assets and eventually leading to decision regards power generation and usage.
In the long run, the implementation of IoT allows electric power companies to improve efficiency, reduce unscheduled downtime, lower costs, and minimize risks related to assets.
Smart Grid
Today, a smart grid envisages the implementation of digital technologies in electric power networks, primarily digital control appliances, and intelligent monitoring systems. An intelligent grid can offer a lot of potential economic and environmental benefits, such as improved reliability of power quality and transmission, enhanced power distribution efficiency, reduced costs for electric utilities, as well as lower gas emissions.
In essence, the modern grid is moving from a one-way system, where power flows from a centralized generation station to customers, to a system that can detect and manage decentralized consumption and production assets, enabling power and information flow in multiple directions.
Applying IoT Technologies in the Electric Power Industry
The electric power industry consists of three core components: power generation, which converts primary energy resources into electricity; power distribution to millions of people; and power transmission, which connects generators to distributors. All these processes can be significantly improved and developed by implementing IoT-embedded systems.
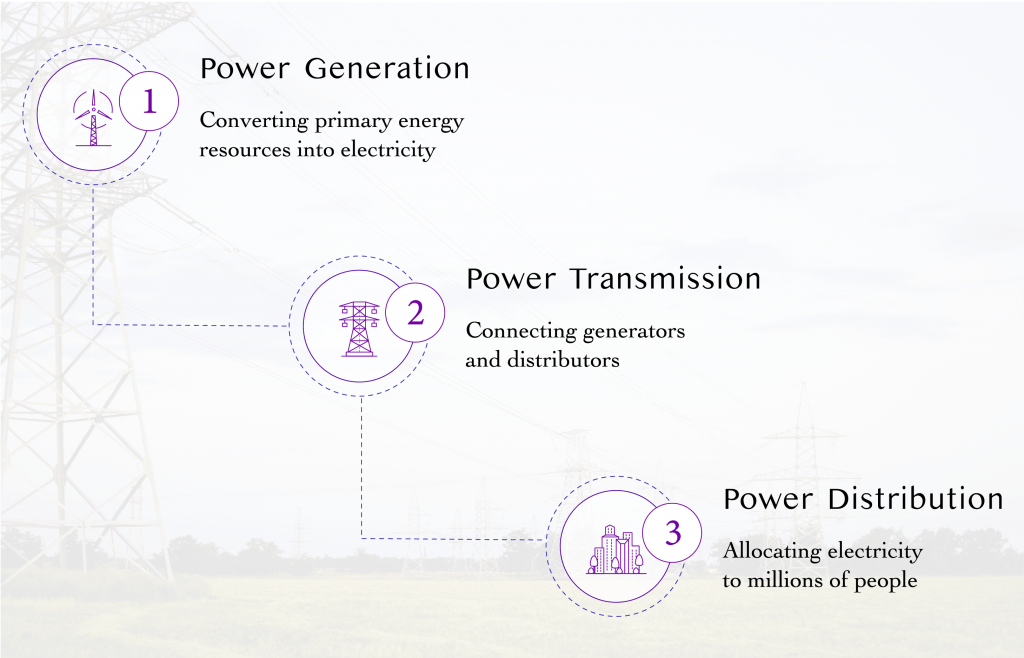
IoT Applications: Energy Generation
Remote Asset Management
IoT-powered asset tracking and management are one of the most promising applications in the power generation context. Such IoT systems connect employees, stakeholders, and assets across the whole business chain into a single network. Moreover, connected sensors embedded in assets are able to measure wear, vibration, tear, temperature, etc., to estimate the overall state of assets from turbines to transmission lines. The adoption of IoT in power generation offers real-time alerts, predictive analytics, automatic reporting, and real-time visibility.
Process Optimization
Smart IoT-powered analytics solutions can significantly improve operational processes, allowing utility companies to achieve better performance and output. IoT system provides real-time data on the overall state of a generation station, therefore contributing to plant automation. Analyzing huge amounts of data in real time, power generation can achieve affordability, sustainability, and availability while reducing the costs of maintenance.
Decentralized Energy Generation
Today, centralized power plants are widely spread, providing most industrialized countries with electricity. However, this centralized approach has been proved inefficient due to energy losses during transmission and lack of reliability guarantee. By contrast, the alternative approach – decentralized electricity generation – appears more reliable and cost-effective. Decentralization in this context means getting power from localized and multiple energy networks.
IoT Applications: Energy Transmission
Asset Maintenance Management
Power transmission and distribution usually include electrical substation equipment, transmission lines, generators, transformers, etc. All this equipment requires constant monitoring in order to prevent faults like overloading, vandalization, etc. IoT- embedded asset management solution allows to monitor and track physical assets and their data. With IoT technologies implemented, asset maintenance systems can detect the sources of failures and faults before the latter becomes crucial, thereby improving the reliability and availability of the assets.
Grid Balancing
The ability of IoT to deliver real-time information can significantly contribute to balancing energy supply and energy demand, effectively managing congestions on transmission and distribution (T&D) lines.
Optimization of Grid Contribution
Renewable energy as a source of electricity generation is gaining traction. According to bp, in 2017, the share of renewable electricity in global electricity generation was up to 8.4 %, constituting almost 50% of the growth in global power generation. IoT also found its place in this context. By implementing an IoT-powered system for grid contribution, excess energy generated by solar panels at the rooftops or wind plants can be redistributed and sold to the grid.
IoT Applications: Energy Consumption
Intelligent Decision Making
With IoT-powered smart meters, internet-connected devices that share data on electricity consumption with a utility company, consumers can become more energy-efficient. Based on the information provided by IoT systems and smart meter mobile apps, they can make smart decisions regarding electricity usage and take appropriate steps to tune their consumption.
Smart Electricity Metering for Smart Homes
By applying various IoT applications, the electric power industry can dynamically adjust the tariffs to consumers, providing them with diverse tariffs and plans to subscribe to.
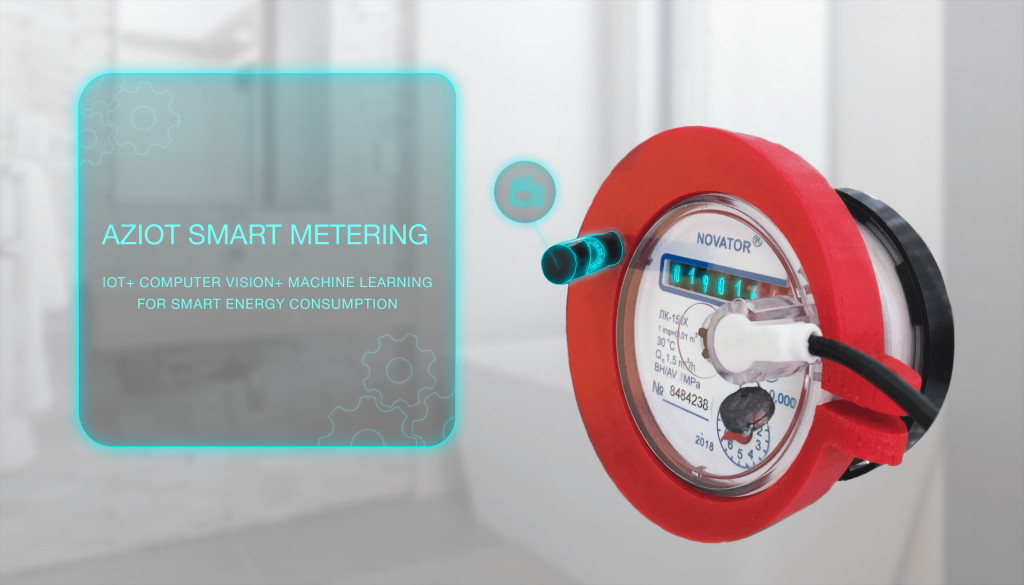
Softengi went further than just creating a device. We have developed a concept that generates an incredible tandem of efficiency and reduced production and maintenance costs. Now consumers do not need to change their meters to new devices, which is quite expensive. Now you can only install a miniature device, which in real-time will be able to track the amount of consumed electricity. With the help of computer vision technology, photos from the camera are recognized, and already processed data is sent to the cloud. Machine Learning algorithms process the data and send the ready-made reports to the mobile application directly to the client’s phone. Data in the cloud is stored securely and available to the client 24/7.
Zero Net Energy Buildings
“Renewables and IoT are absolutely key for zero energy buildings,” claims Cathy Higgins, research director of New Buildings Institute. “In order to run a zero energy building, the facility manager has to get real-time data. IoT provides real-time data about the production, which is essential, not just for operational aspects, but also for trending and potential demand-response.”
The concept of zero net energy (ZNE) buildings is to bring energy consumed from the utility grid over a period of time close to zero, and IoT can significantly contribute to moving us closer to it. Smart control of energy usage provided by IoT can help us to achieve home energy automation.
In Conclusion
IoT has the potential to transform the electric power industry significantly. It is all about the connection of assets, data, and technology personalization. More and more devices and sensors are being connected to the digital world. By using post-time and real-time information with analytics, IoT can enhance the reliability of assets, reduce operational costs, and eliminate unplanned downtime, letting electric power companies achieve higher productivity.





